

Pearson Education, Inc., 221 River Street, Hoboken, New Jersey 07030, (Pearson) presents this site to provide information about Cisco Press products and services that can be purchased through this site. SVIs eliminate the need for a default gateway in the hosts. It switches packets faster than using the router-on-a-stick method. What are two advantages of using a Layer 3 switch with SVIs for inter-VLAN routing? (Choose two.) It requires the switchport access vlan vlan-id interface config command.ġ0. It requires the no switchport interface config command. It requires the switchport mode access interface config command. What is a characteristic of a routed port on a Layer 3 switch? (Choose two.) It requires subinterfaces to be configured on the same subnets.ĩ. It requires multiple physical interfaces on a router. What are two disadvantages of using the router-on-a-stick inter-VLAN routing method in a large network? (Choose two.)

Which router-on-a-stick command and prompt on R1 correctly encapsulates 802.1Q traffic for VLAN 20? Subinterfaces have no contention for bandwidthħ. Simpler Layer 3 troubleshooting than with traditional inter-VLAN routing More switch ports required than in traditional inter-VLAN routing Less complex physical connection than in traditional inter-VLAN routing What two statements are true regarding the use of subinterfaces for inter-VLAN routing? (Choose two.)įewer router Ethernet ports required than in traditional inter-VLAN routing What are the steps that must be completed in order to enable inter-VLAN routing using router-on-a-stick?Ĭonfigure the physical interfaces on the router and enable a routing protocol.Ĭreate the VLANs on the router and define the port membership assignments on the switch.Ĭreate the VLANs on the switch to include port membership assignment and enable a routing protocol on the router.Ĭreate the VLANs on the switch to include port membership assignment and configure subinterfaces on the router matching the VLANs.Ħ. The subinterface numbers must match the VLAN ID number.ĥ. The physical interface must have an IP address configured. The no shutdown command must be given on each subinterface. The IP address of each subinterface must be the default gateway address for each VLAN subnet. What is important to consider while configuring the subinterfaces of a router when implementing inter-VLAN routing? Which command should be configured on the subinterface to enable inter-VLAN routing for VLAN 10?Ĥ. Subinterface G0/1.10 on R1 must be configured as the default gateway for the VLAN 10 192.168.10.0/24 network. Traditional routing uses multiple paths to the router and therefore requires STP, whereas router-on-a-stick does not provide multiple connections and therefore eliminates the need for STP.ģ. Traditional routing uses one port per logical network, whereas a router-on-a-stick uses subinterfaces to connect multiple logical networks to a single router port. Traditional routing requires a routing protocol, whereas a router-on-a-stick only needs to route directly connected networks. Traditional routing is able to use only a single switch interface, whereas a router-on-a-stick can use multiple switch interfaces. What distinguishes traditional legacy inter-VLAN routing from router-on-a-stick?
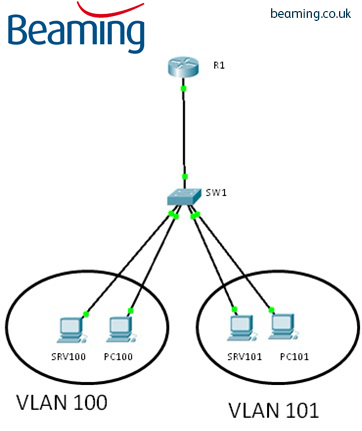
Use a hub to connect the four VLANS with a FastEthernet interface on the router.Ģ. Interconnect the VLANs via the two additional FastEthernet interfaces. Implement a router-on-a-stick configuration. How can this be accomplished using the fewest number of physical interfaces without unnecessarily decreasing network performance?Īdd a second router to handle the inter-VLAN traffic. A router has two FastEthernet interfaces and needs to connect to four VLANs in the local network. The appendix “Answers to the ‘Check Your Understanding’ Questions” lists the answers.ġ. Complete all the review questions listed here to test your understanding of the sections and concepts in this chapter.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
